Viking Runes: The Ancient Alphabet of the Norse People
Viking runes are an essential aspect of Norse history and culture, representing not only a written language but also a system of symbols imbued with mystical and magical significance. These ancient characters, used primarily from the 3rd to the 16th century, were carved into stone, wood, metal, and other materials. The runes held a unique place in Viking society, serving as a medium for communication, divination, and ritual.
The Origins and Development of Runic Alphabets
The runic alphabet, known as the Futhark, is named after its first six letters: F, U, Þ, A, R, and K. The runic system is thought to have originated from the early Germanic tribes and was influenced by the Latin alphabet and the Etruscan script. The earliest runic inscriptions date back to around the 2nd century CE.
There are several versions of the Futhark, reflecting its evolution over time:
-
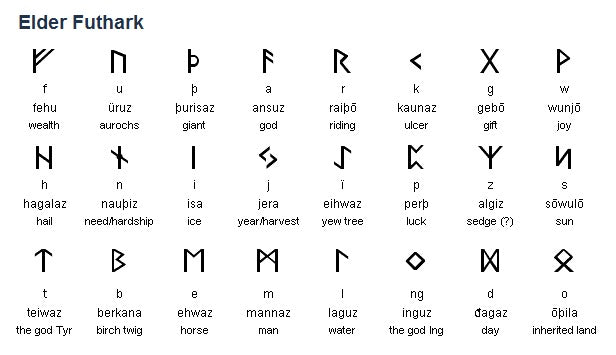
Elder Futhark (c. 2nd to 8th century CE): The oldest form of the runic alphabet, consisting of 24 characters. It was used by the Germanic tribes in Scandinavia and parts of the British Isles. The Elder Futhark inscriptions include a range of texts, from commemorative inscriptions on stones to magical formulas.
-
Younger Futhark (c. 8th to 12th century CE): A simplified version of the Elder Futhark with only 16 characters. This version became prominent in Viking Age Scandinavia and was used in various inscriptions, including runestones and memorials.
-
Anglo-Saxon Futhorc (c. 5th to 11th century CE): An extended version of the Elder Futhark used in Anglo-Saxon England. It included additional characters to represent sounds not present in the original runic alphabet.
The Symbolism and Meaning of Runes
Runes were more than just letters; they were imbued with symbolic meanings and magical properties. Each rune had its own significance and was believed to possess power that could influence the world. Here are some notable runes and their meanings:
-
Fehu (ᚠ): The first rune of the Elder Futhark, representing wealth, prosperity, and cattle. It symbolizes material abundance and the power of possession.
-
Uruz (ᚢ): Symbolizing strength and vitality, Uruz represents the aurochs, a wild ox that was a symbol of power and endurance.
-
Thurisaz (ᚦ): Associated with the giant or thorn, Thurisaz stands for protection and conflict. It also symbolizes the force of chaos and the struggle against it.
-
Ansuz (ᚨ): Representing the god Odin, Ansuz is a rune of divine inspiration and communication. It symbolizes wisdom, knowledge, and the power of the gods.
-
Raidho (ᚱ): This rune signifies travel and journey, both physical and spiritual. It represents the idea of movement, progress, and the path of life.
-
Kenaz (ᚲ): Symbolizing knowledge and enlightenment, Kenaz is associated with the concept of illumination and the light of understanding.
-
Gebo (ᚷ): The rune of gifts and generosity, Gebo represents the concept of exchange, partnership, and the balance of giving and receiving.
-
Nauthiz (ᚾ): Representing need and constraint, Nauthiz signifies the challenges and obstacles that must be overcome.
The Use of Runes in Viking Society
Runes were employed in various aspects of Viking life, from daily communication to magical and ritual practices. Some common uses of runes include:
-
Inscription and Commemoration: Runes were often carved into stones, monuments, and artifacts to commemorate events, individuals, and achievements. These inscriptions served as a form of record-keeping and honoring the dead.
-
Magic and Divination: Runes were used in magical practices and divination. Each rune was believed to have specific powers that could influence the outcome of events or provide guidance. Runes were often cast or drawn to seek answers to questions or predict the future.
-
Ritual and Symbolism: Runes played a significant role in Norse rituals and ceremonies. They were used to invoke the gods, protect against evil, and bring blessings. Runestones and amulets were often inscribed with runes for protection and prosperity.
The Legacy of Runes in Modern Culture
The fascination with runes has endured well beyond the Viking Age. Today, runes are widely recognized and appreciated for their historical and mystical significance. They appear in various forms of popular culture, including literature, films, and games. Modern practitioners of runic magic and Norse paganism also continue to use and study runes, incorporating them into their spiritual and magical practices.
The study of runes has also contributed to the field of historical linguistics and archaeology, providing valuable insights into the language, culture, and beliefs of the Norse people. As symbols of ancient wisdom and power, runes continue to capture the imagination and inspire those interested in the rich tapestry of Norse mythology and history.
Conclusion
Viking runes are a profound and enduring aspect of Norse culture, representing not only a system of writing but also a rich tradition of symbolism and magic. From their origins in the Elder Futhark to their role in Viking rituals and divination, runes hold a special place in the history and legacy of the Norse people. Their continued relevance in modern culture and spiritual practices speaks to the timeless fascination with these ancient symbols and the enduring allure of the Viking Age.
Viking runes, Norse runes, Elder Futhark, Younger Futhark, Anglo-Saxon Futhorc, runic symbolism, Norse mythology, Viking culture, runic inscriptions, rune magic.
